| Indian Passport | |
|---|---|
| Date first issued | 1920 (first version) 1986 (current version) |
| Issued by | India |
| Type of document | Passport |
| Purpose | Identification |
| Eligibility requirements | Indian citizenship |
| Expiration | 10 years (Adult) 5 or 10 years (age 15 to 18) 5 years (Minor) |
| Cost | Adult (36 pages): ₹1,500[1] Adult (60 pages): ₹2,000[1] Minor (36 pages): ₹1,000[1] Note: If the application for a new passport is made under the Tatkaal (expedited processing), the additional Tatkaal fee of ₹2,000 is to be paid in addition to the regular application fee.[1] |
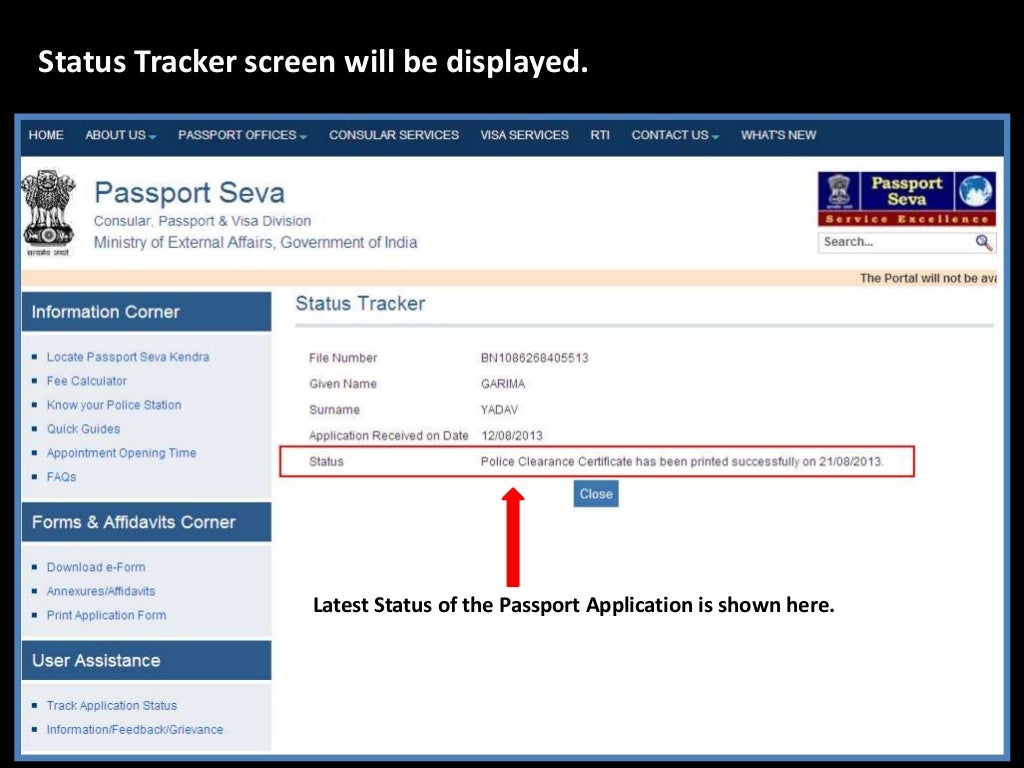
Passport Status India. You can check your current Passport Status below. Just select the type of application and enter your file number, date of birth and click on the Track Status button. You can receive SMS alerts of your Passport Status to receive updates on status changes of your application. A passport reference file number is a number usually provided to someone when they file an application for a passport. The number is useful in tracking the status of their application online and every applicant gets a unique number assigned to them.
An Indian passport is issued by the Indian Ministry of External Affairs to Indian citizens for the purpose of international travel. It enables the bearer to travel internationally and serves as proof of Indian citizenship as per the Passports Act (1967). The Passport Seva (Passport Service) unit of the Consular, Passport & Visa (CPV) Division of the Ministry of External Affairs functions as the central passport organisation, and is responsible for issuing Indian passports on demand to all eligible Indian citizens. Indian passports are issued at 93 passport offices located across India and at 162 Indian diplomatic missions abroad.[2]
In 2015, India issued about 12 million passports, a number exceeded only by China and the United States.[3] Approximately 65 million Indians held valid passports as of the end of 2015.[3]
- 1History
- 2Types of passport
- 3Physical appearance
- 5Issuance
- 6Visa requirements
History[edit]
Passport Application Status
British Raj[edit]
British Indian passports were issued to British subjects of the British Indian Empire, as well as to British subjects from other parts of the British Empire, and subjects of the British protected states in India (i.e. British protected persons of the 'princely states').[4] These passports were introduced in British India after the First World War.[5] The Indian Passport Act of 1920 required the use of passports, established controls on the foreign travel of Indians, and foreigners travelling to and within India.[6] The passport was based on the format agreed upon by the 1920 League of Nations International Conference on Passports.[7] However, the British Indian passport had very limited usage, being valid for travel only within the British Empire, Italy, Switzerland, Austria, Czechoslovakia, Germany, France, Spain, Norway, Sweden and Holland.[8]
Dominion of India[edit]
The use of the passport was discontinued after the establishment of the dominions of India and Pakistan in 1947, and its bearers were entitled to opt for Indian, Pakistani or British nationality. Passport laws were made strict in both the countries in 1952. Citizens of both India and Pakistan did not need a visa or were issued one on arrival until the Second Kashmir War. Before the war, citizens of both countries could freely travel to each other's countries, despite having gone to war in 1947 over Kashmir.[9]
Types of passport[edit]
- Ordinary Passport (Dark Blue) is issued to ordinary citizens for ordinary travel, such as for vacation, study and business trips (36 or 60 pages). It is a 'Type P' passport, where P stands for Personal.
- Official Passport (White cover) is issued to individuals representing the Indian government on official business. It is a 'Type S' passport, S stands for Service.
- Diplomatic Passport (Maroon cover) is issued to Indian diplomats, top ranking government officials and diplomatic couriers. It is a 'Type D' passport with D stands for Diplomatic.
In addition, selected passport offices in India as well as overseas missions were authorised to issue regular Indo-Bangladesh passports and Indo-Sri Lankan passports to Indian nationals resident in West Bengal, the North-Eastern States, Tamil Nadu and Puducherry. These two passports respectively permitted travel to Bangladesh and Sri Lanka only and were not valid for travel to other foreign countries. India stopped issuing the Indo-Bangladeshi passport in 2013.[10]
Tatkaal and SVP[edit]
Tatkaal Passports (for urgent needs),[11] and Short Validity Passport (SVP)[12] are also available and these are generally considered Ordinary Passports once issued.
Physical appearance[edit]
Contemporary ordinary Indian passports have a black or deep bluish-black cover with golden coloured printing. The Emblem of India is emblazoned in the centre of the front cover. The words 'पासपोर्ट' in Devanagari and 'Passport' in English are inscribed above the Emblem whereas 'भारत गणराज्य' in Devanagari and 'Republic of India' in English are inscribed below the emblem. The standard passport contains 36 pages, but frequent travellers can opt for a passport containing 60 pages. Some early passports were handwritten, including some issued between 1997 and 2000 with 20 year validity dates. These passports have been ruled invalid by the Indian government and holders must replace them with machine-readable versions good for 10 years due to ICAO regulations.[13]
Identity Information Page[edit]
- The Bio data page contains the following information:
- Type: 'P'- Stands for 'Personal', 'D'- Stands for 'Diplomatic', 'S'- Stands for 'Service'
- Country code: IND
- Passport number
- Surname
- Given name(s)
- Nationality: Indian
- Sex
- Date of birth
- Place of birth
- Place of issue
- Date of issue
- Date of expiry
- Photo of passport holder
- Ghost picture of the passport holder (only passports issued since 2013)
- Signature of the passport holder
- The information page ends with the Machine Readable Passport Zone (MRZ).
- The Demographics page at the end of the passport book contains the following information:
- Name of father or legal guardian
- Name of mother
- Name of spouse
- Address
- Old passport number
- File number
Passport note[edit]
All passports contain a note in Hindi and English, nominally from the President of India, addressing the authorities of all countries and territories:
| “ | इसके द्वारा, भारत गणराज्य के राष्ट्रपति के नाम पर, उन सब से जिनका इस बात से सरोकार हो, यह प्रार्थना एवं अपेक्षा की जाती है कि वे वाहक को बिना रोक-टोक, स्वतंत्रतापूर्वक आने-जाने दें, और उसे हर प्रकार की ऐसी सहायता और सुरक्षा प्रदान करें जिसकी उसे आवश्यकता हो ।
| ” |
| “ | These are to request and require in the Name of the President of the Republic of India all those whom it may concern to allow the bearer to pass freely without let or hindrance, and to afford him or her, every assistance and protection of which he or she may stand in need.
| ” |
The note bearing page is typically stamped and signed by the issuing authority in the name of the President of the Republic of India.
Languages[edit]
The text of Indian Passport is printed in both Hindi and English, two official languages of India.
Emigration check[edit]
Holders of Emigration Check Required (ECR) type passports need a clearance called an Emigration Check from the Government of India's Protector of Emigrants when going to selected countries on a work visa. This is to prevent the exploitation of Indian workers (especially the unskilled and less-educated) when going abroad, particularly to Middle Eastern countries. ECR type passport holders travelling on a tourist visa do not need a clearance; this is known as an Emigration Check Suspension.
Emigration Check Not Required (ECNR) status passports are granted to:
- Indian nationals born abroad;
- Indian nationals holding at least a matriculation certificate;
- All holders of diplomatic or official passports.
- All gazetted government servants;
- All income-tax payers (including agricultural income-tax payers) in their individual capacity;
- All graduate and professional degree holders (such as doctors, engineers, chartered accountants, scientists, lawyers, etc.);
- Spouses and dependent children of category of certain holders of ECNR passports;
- Seamen in possession of a CDC;
- Sea Cadets and Deck Cadets who have:
- Passed their final examination on a three-year B.Sc. Nautical Sciences Course at T.S. Chanakya, Mumbai; and
- Undergone three months' pre-sea training at any of the government-approved training institutes such as T.S. Chanakya, T.S. Rehman, T.S. Jawahar, MTI (SCI), or NIPM, Chennai, after production of identity cards issued by the Shipping Master at Mumbai, Kolkata, or Chennai;
- Persons holding a Permanent Immigration Visa, such as visas issued by the UK, USA, or Australia;
- Persons possessing a two years' diploma from any institute recognized by the National Council for Vocational Training (NCVT) or the State Council of Vocational Training (SCVT), or persons holding a three years’ diploma or equivalent degree from an institution such as a polytechnic recognized by the central or a state government;
- Nurses possessing qualifications recognised under the Indian Nursing Council Act, 1947;
- All persons above the age of 50 years;
- All persons who have been staying abroad for more than three years (whether in one continuous period or in aggregate), as well as their spouses;
- All children up to the age of 18 years.
In accordance with a ruling by the Ministry of External Affairs, passports issued from 2007 onwards do not have the ECNR stamp affixed; instead, a blank page 2 of the passport is deemed to have been ECNR endorsed. As a result, only ECR stamps are now affixed to Indian passports. For passports issued before January 2007, no notation in the passport means ECR. For passports issued in or after January 2007, no notation in the passport means ECNR. If Emigration Check is Required, there will be an endorsement in the passport regarding ECR.
Features[edit]
Since 25 November 2015, Indian passports that are handwritten or with an original date of expiry extending to 20 years have not been valid under ICAO travel regulations.[14] With more recent Indian passports the personal particulars of the passport holder, that were hitherto printed on the inner cover page, are printed on the second page of the document. Another added security feature in the newer non-handwritten passports is a ghost picture of the holder found on the right side of the second page. Apart from stymieing criminals from printing fake passports, recent changes also help prevent smudging of the document because of inkjet printers.[15][16]
Fees[edit]
The price of a standard passport in India:[17]
- ₹1500 – Fresh issuance or reissue of passport (36 pages, standard size) with 10 year validity.
- ₹2000 – Fresh issuance or renewal of passport (60 pages, 'jumbo' size) with 10 year validity.
- ₹3500 – First time applicant or renewal with expedited ('tatkaal') service (36 pages) with 10 year validity.
- ₹4000 – First time applicant or renewal with expedited ('tatkaal') service (60 pages) with 10 year validity.
- ₹1000 – Fresh passport issuance for minors (below 18 years of Age) with 5 year validity or till the minor attains the age of 18, whichever is earlier.
- ₹3000 – Duplicate passport (36 pages) in lieu of lost, damaged or stolen passport.
- ₹3500 – Duplicate passport (60 pages) in lieu of lost, damaged or stolen passport.
Indian passports can also be issued outside India, for which fees varies by country.
Issuance[edit]
Passport Seva Kendra[edit]
In September 2007, the Indian Union cabinet approved a new passport issuance system under the Passport Seva Project. As per the project, front-end activities of passport issuance, dispatch of passports, online linking with police, and Central Printing Unit for centralised printing of passports will be put in place. The new system is trying to be 'timely, transparent, more accessible and reliable manner' for passport issuance. The applicant has to apply for fresh/reissue of passport through the Passport Seva system at one of the 77 Passport offices known as 'Passport Seva Kendra's operating throughout the country.
Biometric passport[edit]
India has recently initiated the first phase of biometric e-passport for Diplomatic passport holders in India and abroad. The new passports have been designed locally by the Central Passport Organisation, the India Security Press and IIT Kanpur. It contains a security chip with all personal data and digital images. In the first phase new passports will have a 64KB chip carrying a photograph of the passport holder and in subsequent phases it will have a fingerprint. The new passport has already been tested with passport readers in the United States and has 4-second response time, while the US Passport has 10-second response time. It need not be carried in a metal jacket for security reasons. It will first need to be skimmed through a reader, after which it would generate an access code which then unlocks the chip for reader access.[18]
In India, the e-passport is under its first phase of deployment and is restricted to Diplomatic passport holders. On 25 June 2008 the Indian Passport Authority issued the e-passport to the then President of India Pratibha Patil.[19] As of 2016, the Government has plans to issue e-passports to all of its citizens. Also the Government has authorized Indian Security Press to float a global three-stage tender for procurement of ICAO-compliant electronic contactless inlays along with its operating system, which is required for the manufacture of biometric Passports.[20] The necessary procurement have been initiated by India Security Press, Nasik by calling for Global tender for the supply of electronic contactless inlays.[21] The actual transition to the new age passport is expected to commence on the successful completion of the tendering and procurement process.[22]
Visa requirements[edit]
Visa requirements for Indian citizensVisa requirements for Indian citizens are administrative entry restrictions by the authorities of other states placed on citizens of India. As of February 2019, Indian citizens had visa-free or visa on arrival access to 61 countries and territories, ranking the Indian passport 79th in terms of travel freedom according to the Henley Passport Index.[23] Furthermore, Indian citizens may live and work freely in Nepal under the terms of the 1950 Indo-Nepal Treaty of Peace and Friendship.
Foreign travel statistics[edit]
According to the statistics these are the numbers of Indian visitors to various countries in 2017(unless otherwise noted)
Govt Of India Pan Card
| Foreign travel statistics | |
|---|---|
| Destination | Number of visitors |
| American Samoa[note 1][24] | 63 |
| Angola[25] | 9,170 |
| Antarctica[note 2][26] | 292 |
| Antigua and Barbuda[note 2][27] | 366 |
| Australia[note 2][28] | 302,200 |
| Austria[note 3][note 1][29] | 147,300 |
| Azerbaijan[note 1][30] | 6,012 |
| Barbados[note 3][note 1][31] | 900 |
| Belgium[note 1][32] | 44,898 |
| Bhutan[note 2][33] | 172,751 |
| Bolivia[note 1][34] | 1,338 |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina[note 2][35] | 1,700 |
| Botswana[36] | 17,413 |
| Brazil[note 2][37] | 16,916 |
| Cambodia[note 1][38] | 46,131 |
| Canada[note 2][39] | 261,801 |
| Cayman Islands[note 2][note 4][40] | 292 |
| Chile[note 2][41] | 4,468 |
| China[note 1][42][43] | 799,100 |
| Colombia[44] | 5,402 |
| Congo[note 5][45] | 2,373 |
| Costa Rica[note 2][46] | 7,415 |
| Croatia[note 2][47] | 55,745 |
| Cuba[note 2][47] | 2 |
| Dominica[48] | 97 |
| Dominican Republic[note 2][49] | 4,649 |
| France[50] | 524,055 |
| French Polynesia[note 2][51] | 379 |
| Georgia[note 2][52] | 59,732 |
| Germany[note 1][53] | 231,244 |
| Guam[note 2][note 4][54] | 8 |
| Hong Kong[note 2][55] | 392,853 |
| Hungary[note 3][note 1][56] | 33,134 |
| Indonesia[note 1][57] | 422,045 |
| Israel[note 2][58] | 58,000 |
| Italy[note 1][59] | 225,000 |
| Jamaica[note 2][60] | 1,834 |
| Japan[61] | 103,084 |
| Jordan[note 1][62] | 57,720 |
| Kazakhstan[note 2][63] | 21,890 |
| Kyrgyzstan[note 2][64] | 19,600 |
| Laos[note 2][65] | 4,343 |
| Latvia[note 3][note 2][66] | 5,476 |
| Lebanon[note 1][67] | 15,610 |
| Macao[note 2][68] | 148,121 |
| Madagascar[69] | 2,234 |
| Malaysia[note 2][70] | 552,739 |
| Maldives[note 2][71] | 83,019 |
| Mali[note 6][72] | 1,500 |
| Mauritius[note 2][71] | 86,294 |
| Mexico[note 1][73] | 59,020 |
| Mongolia[note 2][74] | 1,888 |
| Montenegro[note 6][note 3][75] | 1,131 |
| Myanmar[76] | 34,628 |
| Nepal[note 7][77] | 75,124 |
| Netherlands[note 2][78] | 155,000 |
| New Zealand[note 2][79] | 61,440 |
| Oman[note 2][80] | 321,161 |
| Panama[81] | 6,748 |
| Papua New Guinea[note 1][82] | 4,293 |
| Peru[note 2][83] | 7,201 |
| Philippines[note 2][84] | 107,278 |
| Qatar[note 2][85] | 333,708 |
| Romania[note 1][86] | 16,753 |
| Russia[note 2][87] | 130,400 |
| Seychelles[note 2][88] | 13,518 |
| Singapore[note 2][89] | 1,272,069 |
| Slovakia[note 1][note 3][90] | 6,805 |
| South Africa[91] | 85,639 |
| South Korea[note 2][92] | 123,416 |
| Spain[note 2][93] | 141,122 |
| Sri Lanka[note 1][94] | 356,729 |
| Suriname[note 2][95] | 1,045 |
| Swaziland[note 1][96] | 6,867 |
| Taiwan[note 2][97] | 40,846 |
| Tanzania[note 1][98] | 69,876 |
| Thailand[note 2][99] | 1,411,942 |
| Timor-Leste[note 6][note 7][100] | 799 |
| Turkey[note 2][101] | 86,996 |
| Ukraine[note 2][102] | 23,173 |
| United Arab Emirates[note 2][103] | 2,073,000 |
| United Kingdom[note 2][104] | 525,000 |
| United States[note 2][note 8][105] | 2,055,480 |
| Uzbekistan[note 9][106] | 18,100 |
| Zambia[107] | 25,517 |
| Zimbabwe[108] | 5,421 |
- ^ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuData for 2016
- ^ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzaaabacadaeafagahaiajakalamanaoapaqarasatauData for 2017
- ^ abcdefCounting only guests in tourist accommodation establishments.
- ^ abData for arrivals by air only.
- ^Data for 2012
- ^ abcData for 2014
- ^ abData for arrivals by air only.
- ^Total number includes tourists, business travelers, students, exchange visitors, temporary workers and families, diplomats and other representatives and all other classes of nonimmigrant admissions (I-94).
- ^Data for 2015
Gallery of historic images[edit]
British Indian passport issued during the colonial days
Indian passport, valid only for India-Pakistan travel, issued to migrants to enable them to visit family, friends and ancestral homes located on the other side of the Radcliffe line
Passport issued by the Dominion of India (1947–1950)
Cover of a passport (1986)
Indian Diplomatic passport and Indian Official passport
See also[edit]
References[edit]
Passport Application Status Online India
- ^ abcd'Fee Structure : Document Advisor - Passport Seva'. passportindia.gov.in. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'MEA CPV Division'. CPV.
- ^ ab'India ranks third in issuing passports - Times of India'. Times of India. 1 January 2016. Archived from the original on 2 January 2016. Retrieved 29 January 2016.
- ^'Dominions 1931-1947'. Historical Atlas of the British Empire. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ^MumbaiSpace Indian Passport HistoryArchived October 6, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^Passport (Entry into India) Act, 1920 (No. 34 of 1920)
- ^History of Passports
- ^Vazira Fazila-Yacoobali Zamindar (2007). The Long Partition and the Making of Modern South Asia. Columbia University Press. p. 162. ISBN0-231-13846-6.
- ^https://www.dawn.com/news/1283918
- ^'41-year-old India-Bangladesh passport regime ends'. Times of India. 2 December 2013.
- ^Tatkaal passports. 'Tatkaal passports'. www.passportindia.gov.in. CPV, Government of India. Retrieved 22 April 2017.
- ^'Passport Seva Miscellaneous Queries'. passportindia.gov.in. CPV, Government of India. Retrieved 22 April 2017.
- ^https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/invalid-but-over-a-lakh-indian-handwritten-passports-still-in-circulation/story-CL9WfD5z1nOi8idmpSRptM.html
- ^the Times of India website article accessed 29 January 2016
- ^Oppili, P. (12 April 2013). 'New passports with added security features dispatched'. Retrieved 26 March 2018 – via www.thehindu.com.
- ^'A ghost in your passport to make it tamper-proof - Times of India'.
- ^'Indian Passport Fees'(PDF). Government of India. Retrieved 19 December 2012.
- ^'NDTV.com: After US tests, India to get first e-passport'. ndtv.com. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'India to introduce biometric passports next year'. secureidnews.com. 5 July 2012. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- ^'India to introduce biometric passports to all of it's Citizens'. Ministry of External Affairs, Parliament Q&A – 1724. 27 July 2016.
- ^'Indian Security Press Global Tender for Supply Electronic contactless inlays'(PDF). Indian Security Press- Nashik, Tender No-54/2016-17. 27 July 2016.
- ^'India looks to Biometric Passports'. Security Documentworld.com. 28 July 2016.
- ^'Henley Passport Index 2006 to 2019'. Henley & Partners. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- ^'Statistical Yearbook - Department of Commerce'.
- ^Anuário de Estatística do Turismo
- ^'Tourism Statistics - IAATO'. iaato.org. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'Tourism Statistics for Antigua and Barbuda'. antiguahotels.org. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^[1]
- ^'Archived copy'(PDF). Archived from the original(PDF) on 14 February 2017. Retrieved 30 May 2017.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
- ^'Number of foreign citizens arrived to Azerbaijan by countries'.
- ^https://corporate.visitbarbados.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/2016-annual-statistical-report.pdf
- ^'Tourisme selon pays de provenance 2016'.
- ^Namgay, Phunstho. 'Annual Reports - Tourism Council of Bhutan'. www.tourism.gov.bt.
- ^'INE - Instituto Nacional de Estadística - Turismo'.
- ^TOURISM STATISTICS Cumulative data, January – December 2017
- ^'Statistics Botswana'. Statistics Botswana. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^http://dadosefatos.turismo.gov.br/2016-02-04-11-53-05/item/download/784_28e96970a52eb457d54bb9c5f454029a.html
- ^'Tourism Statistics Report'. www.tourismcambodia.org. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'Service bulletin International Travel: Advance Information'(PDF). statcan.gc.ca.
- ^CIDOT. 'Welcome to the Cayman Islands Department of Tourism (CIDOT) Destination Statistics Website'. www.caymanislands.ky. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^Mehta, Shriji (18 October 2018). 'Documents Required for Passport in India'. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
- ^'China Inbound Tourism Statistics in 2015'. www.travelchinaguide.com. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'Tourists in China by country of origin 2016 - Statistic'. Statista.
- ^The data obtained on request. Ministerio de Comercio, Industria y Turismo de Colombia
- ^[2]
- ^'Informes Estadísticos - Instituto Costarricense de Turismo - ICT'. www.ict.go.cr. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^ abTOURIST ARRIVALS AND NIGHTS IN 2017
- ^'2015 Visitors Statistics Report'(PDF). tourism.gov.dm. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'BCRD - Estadísticas Económicas'. www.bancentral.gov.do. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^[3]
- ^'Données détaillées'. www.ispf.pf. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'International arrivals 2017'.
- ^Tourismus in Zahlen 2016, Statistisches Bundesamt
- ^'Visitor Arrival Statistics - Research - Research and Reports'. www.guamvisitorsbureau.com. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^[4]
- ^'TOURISM IN HUNGARY 2016'.
- ^[5]
- ^TOURIST ARRIVALS TO ISRAEL (EXC. DAY VISITORS & CRUISE PASSENGERS) BY NATIONALITY, Ministry of Tourism
- ^'IAGGIATORI STRANIERI NUMERO DI VIAGGIATORI'.
- ^Monthly Statistical Report December 2017 Vol xxvii No 12
- ^'2015 Foreign Visitors & Japanese Departures'(PDF). jnto.go.jp. Japan National Tourism Organization. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'Tourist Overnight and Same Day Visitors By Nationality during'.
- ^'Статистические сборники'. stat.gov.kz.
- ^'Туризм в Кыргызстане - Архив публикаций - Статистика Кыргызстана'. www.stat.kg.
- ^'Statistical Reports on Tourism in Laos'.
- ^'TUG02. Visitors staying in hotels and other accommodation establishments by country of residence-PX-Web'. csb.gov.lv. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'Arrivals according to nationality during year 2016'.
- ^'DSEC - Statistics Database'. www.dsec.gov.mo. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'Publications - Statistiques'. tourisme.gov.mg. 27 May 2015. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'TOURIST ARRIVALS TO MALAYSIA BY COUNTRY OF NATIONALITY DECEMBER 2017'(PDF). tourism.gov.my. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^ ab'December 2017 - Ministry of Tourism'. www.tourism.gov.mv. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^ANNUAIRE 2014
- ^'Visitantes internacionales por vía aérea por principal nacionalidad'. sectur.gob.mx. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^[6]
- ^'Table 4. Foreign tourist arrivals and overnight stays by countries, 2014'(PDF). monstat.org. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'Myanmar Tourism Statistics 2015'(PDF). Central Statistical Organization. Ministry of National Planning and Economic Development. Archived from the original(PDF) on 29 December 2016. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ^Tourism Statistics 2015 p.20,31Archived 31 January 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^Toerisme in perspectief 2018
- ^'International travel and migration: December 2017'. Statistics New Zealand. Retrieved 2 February 2018.
- ^[7]
- ^[8]
- ^[9]
- ^'datosTurismo'. datosturismo.mincetur.gob.pe.
- ^[10]
- ^'2016 Annual Tourism Performance Report'(PDF). visitqatar.qa. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^[11]
- ^'Въезд иностранных граждан в РФ'. Fedstat.ru. 18 October 2017. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^[12]
- ^'Visitor Arrivals'. www.stb.gov.sg. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^[13]
- ^[14]
- ^'Korea, Monthly Statistics of Tourism - key facts on tourism - Tourism Statistics'. kto.visitkorea.or.kr. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'Tabla23984'. www.ine.es. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'TOURIST ARRIVALS BY COUNTRY OF RESIDENCE 2016'(PDF). sltda.gov.lk. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'Suriname Tourism Statistics'(PDF). www.surinametourism.sr. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
- ^'Swaziland Tourism - Swaziland Safari - Swaziland Attractions - Useful Links - Research'. www.thekingdomofswaziland.com. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'Visitor Arrivals by Nationality'. taiwan.net.tw. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'The 2016 International Visitors' Exit Survey Report. International Tourist Arrivals. pp. 73–77'(PDF). nbs.go.tz/. NBS Tanzania. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- ^'สถิติด้านการท่องเที่ยว ปี 2560 (Tourism Statistics 2017)'. Ministry of Tourism & Sports. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
- ^[15]
- ^'NUMBER OF ARRIVING-DEPARTING VISITORS, FOREIGNERS AND CITIZENS December 2017'.
- ^'Foreign citizens who visited Ukraine in 2017 year, by countries'.
- ^Statistics for the Emirate of Dubai
Dubai Statistics, Visitor by Nationality - ^'Annual estimates on visits and spending in the UK by overseas residents, by purpose and region of visit'. Office of National Statistics.
- ^'Table 28. Nonimmigrant Admissions (I-94 Only) By Selected Category Of Admission And Region And Country Of Citizenship: Fiscal Year 2016'. dhs.gov. 16 May 2017. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- ^'Распределение въехавших в Республику Узбекистан иностранных граждан по странам в 2015 году'. data.gov.uz. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- ^'Tourism Statistical Digests'.
- ^'Tourism Trends and Statistics 2015 Annual Report – Zimbabwe A World Of Wonders'. www.zimbabwetourism.net. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Passports of India. |